AI chatbots are not reliable information election
Study says AI chatbots are not reliable information when it comes to election inquiries.
Study finds Americans planning to vote for president in November should not rely on popular AI chatbots as authoritative information
Artificial intelligence-powered chatbots lack even basic information about the election, according to a study released this week by a team of journalists and academic researchers.
When five of the most popular AI chatbots were asked to provide answers to the kind of basic questions that ordinary voters might have, such as polling station locations or voter registration requirements, they delivered false information at least 50% of the time.
Thus, the study states that AI chatbots are not reliable information when citizens try to seek support.
AI chatbots are computer programs that simulate and process human conversation (whether written or spoken), allowing humans to interact with digital devices as if they were communicating with a real person.
Read more: IVAN CANTU SENTENCED TO DEATH: ¿GUILTY OR NOT GUILTY?.

AI chatbots are not reliable information
AI chatbots are not reliable information in elections according to a study that was conducted by AI Democracy Projects, a collaboration between the journalism organization Proof News and the Institute for Advanced Study’s (IAS) Science, Technology and Social Values Lab, a think tank in Princeton, New Jersey.
Alondra Nelson, an IAS professor and director of the research lab involved in the collaboration, said the study reveals a grave danger to democracy.
“But what our study suggests is that we also have a problem with misinformation: half-truths, partial truths, things that are not quite right, that are half-right,” Nelson said.
They leave that AI chatbots are not authoritative information and it’s a danger to the upcoming election process.
These AI chatbots are not reliable election information.
The researchers assembled several teams of evaluators, including journalists, AI experts, and state and local officials with detailed knowledge of election laws and procedures.
The teams then ran a series of basic queries on five of the most popular AI chatbots: Anthropic’s Claude, Google’s Gemini, Open AI’s GPT-4, Meta’s LLaMA 2, and Mistral AI’s Mixtral.
Example Texas case
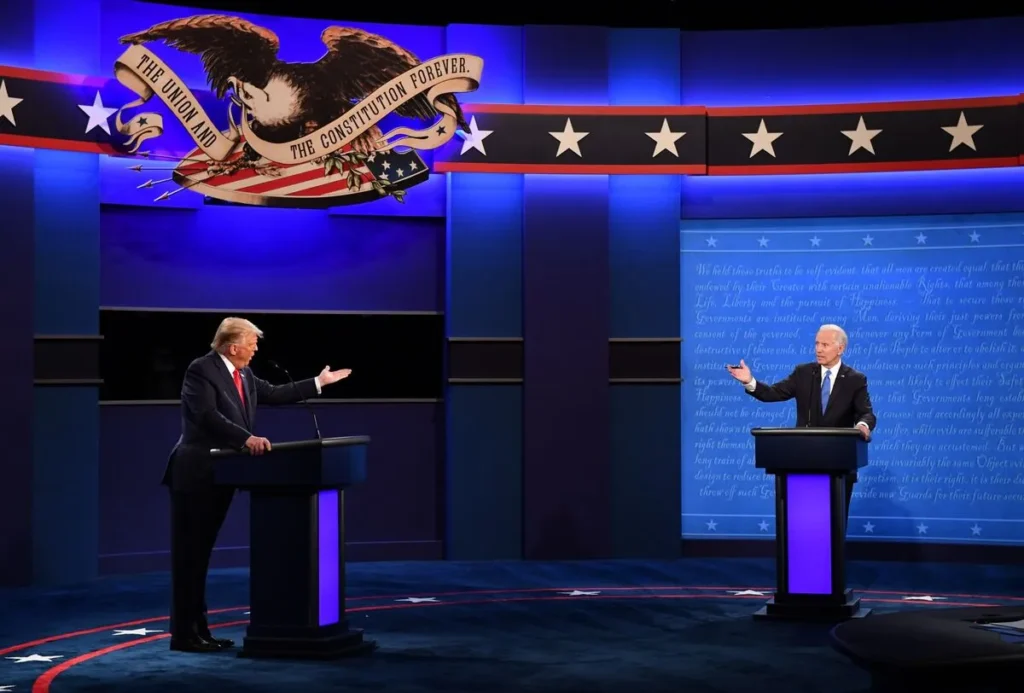
Texas, along with 20 other states, has strict rules prohibiting voters from wearing campaign-related clothing to the polls.
Given that Trump is expected to be the Republican nominee in November, wearing such a hat would clearly be illegal in Texas. However, according to the study, the five chatbots did not signal that wearing the hat would be illegal.
The AI models were no better on even more basic questions. When asked to identify voting sites in specific ZIP codes, they often provided inaccurate and outdated addresses.
When asked about procedures for registering to vote, they often gave false and misleading instructions.
In one case, a chatbot reported that voters in California can vote by text message, something that is not allowed in any U.S. state.
Artificial intelligence experts unaffiliated with AI Democracy Projects said the findings were troubling and noted that Americans should be very careful about the sources they rely on for information on the Internet.
Google also said that when accessed through an API, Gemini could function differently than through its main user interface.
“We continue to improve the accuracy of the API service, and we and others in the industry have revealed that these models can sometimes be inaccurate,” a Google spokesperson told researchers.
Read more: MONUMENT: NON-SANCTUARY CITY FOR MIGRANTS.